TLDR
This guide on crypto margin trading is aimed at intermediate traders who want to increase their profit potential using borrowed funds from margin trading exchanges. It goes in-depth into a step-by-step approach to how to find the best trading opportunities and how to execute them.
The guide also covers critical concepts a margin trader must understand before risking money. Here is a quick overview of a trader’s steps to execute a trade.
- Step 1: Choose a crypto margin trading Platform and Open an Account.
- Step 2: Deposit funds to borrow against.
- Step 3: Choose trading pairs with appropriate liquidity.
- Step 4: Place a long or short order depending on the price action.
- Step 5: Put a stop loss as part of risk management on the order.
- Step 5: Take profits at predetermined levels.
What is Margin Trading?
Margin trading is when you borrow money from a 3rd party to enter larger positions than a trader’s portfolio allows. How much a trader can borrow will depend on the portfolio size and the leverage on the position. Many trading platforms allow leverage up to 100x or even more, exponentially increasing your profit potential.
However, margin trading comes with its own set of risks. Leveraged trading is often considered a double-edged sword. It’s simply because the leverage can wreck your portfolio if you misjudge the price movement. This is why proper risk management is crucial to start margin trading.
Margin Trading in Crypto
The core concept of margin trading remains the same for cryptocurrencies. However, economists agree that digital assets are riskier for margin trading due to their high volatility. In case you’re unaware, cryptocurrencies are decentralized and largely unregulated, quickly creating extreme highs and lows.

It means no central authority regulates the price and protects investors in case of extreme price movements. This increases the risks of forced liquidation on a trader’s margin account.
How to Margin Trade on Binance?
Binance is currently the largest cryptocurrency trading platform in the world. So, we’re using it as an example.
If you’re not confident in Binance margin trading, you can always go for margin trading at Bybit, Kraken, or any other exchange.
Step 1: Open a Margin Trading Account
To open a margin trading account on Binance, click the [Get Started] button.


More details
Binance is a great combination of low fees, deep liquidity and multiple cryptocurrencies and trading pairs. We have tested every aspect of it and it STILL holds its reign as the top exchange in the world. In our view, it is the perfect crypto exchange for both newbies and advanced traders alike.
-
Biggest exchange in the world.
-
Industry's lowest trading fees.
-
Advance trading options like leverage trading.
-
600+ crypto options, 150+ for the US.
-
Lucrative on-site staking options.
-
Hiccups in account verification.
-
Less regulated than some competitors.
-
The corporate structure is not transparently.
On Binance, you don’t need a separate margin account. A general account gives you access to spot trading, crypto margin trading, and futures trading on different pairs.
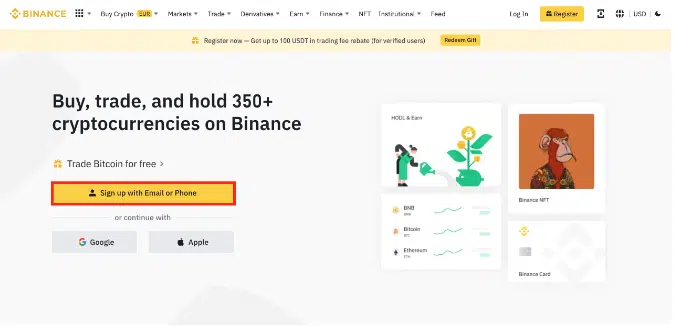
Visit the Binance website, click [Sign Up], and complete the registration form, followed by KYC verification.
If you don’t have a Binance account, follow this easy step-by-step guide.
Step 2: Deposit Funds
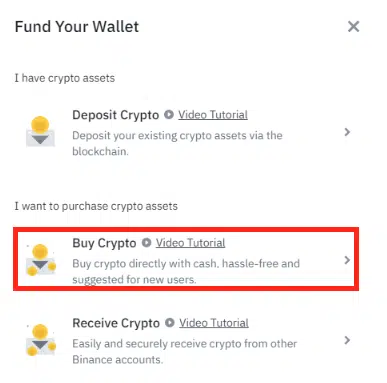
To borrow funds from Binance, you first need collateral. If you already have crypto tokens like BTC or stablecoins like USDT, transfer the funds to your Binance wallet. If you don’t, Binance lets you buy crypto directly with fiat money.
Step 3: Choose Trading Pair on Margin
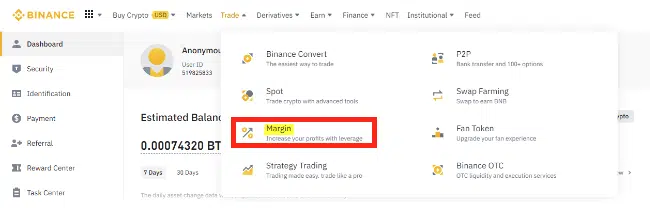
On the main navigation menu on the top section of the page, go to [Trade] and choose [Margin]. The margin trading window will appear on your screen. Choose the trading pair.
Step 4: Choose Leverage for the Position
After selecting the trading pair, choose what type of leverage you want. Cross and isolated are the offered options. We have a discussion coming up on how each type works. Choose your collateral size from the same menu.
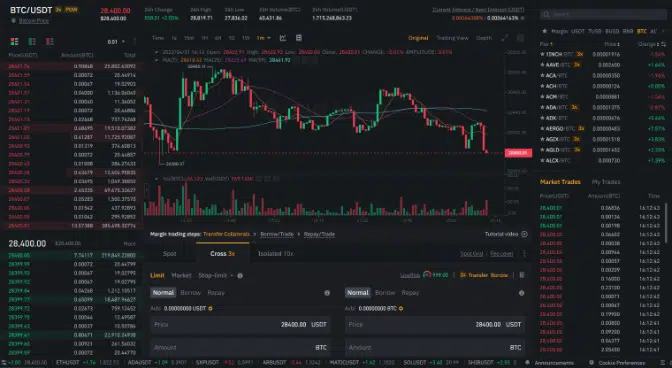
Step 5: Place the Order
Once you’re satisfied with the settings for the trade, place a market order or a limit order.
Important Concepts You Must Understand
Margin trading is unsuitable for beginners or investors who haven’t spent enough time comprehending the dynamics in the derivatives trading space. The borrowing of funds adds an extra layer of risk to uninformed traders.
Thankfully, gathering information is no longer rocket science in this era of information technology. We have gathered the most important concepts you must understand before you graduate to margin trading crypto from spot trading.
Leveraged Trading
Leverage trading is perhaps the most crucial concept for any margin trader to understand. A crypto exchange allows you to “leverage” your position size of margin trade for greater gains. For example, a 5x leverage means you’re increasing your position size by five times to generate a five times larger profit using borrowed funds from the crypto exchange.
So, if a digital asset, BTC, increases or decreases in price by 5%, your profit will be 25% based on whether you opened a long or short position. It’s a great way to generate quick profits with small price movements in day trading.
The reason leverage is a double-edged sword is that if the price moves 5% in the wrong direction, the trader will be in a 25% loss instead of only a 5% loss. Hence, managing risk for margin trades and avoiding maximum leverage is critical.
Position Size
The position size is the collateral you place to borrow funds from the crypto exchanges. This currency (USD/GBP/EUR) must be in your margin account to make margin trading work. The leverage value adjusts automatically depending on your position size, as the lender will always protect its funds.
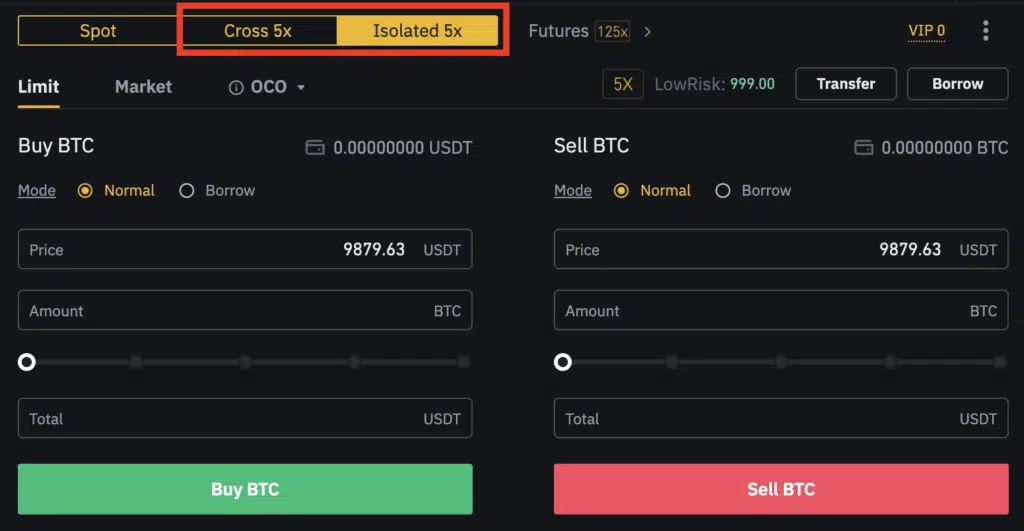
Cross Margin Trading vs. Isolated Margin Trading
As you introduce leverage, you must understand cross-margin and isolated-margin trading.
A “cross” margin is when your margin balance is shared across all open positions. In other words, the remaining balance in your account will work as a source of funds to prevent liquidation in case of bad trades.
Isolated margin trading “isolates” the margin for a particular position. The remaining account balance will be safe in liquidation with a secluded margin position.
If you’re wondering which is the better option for leveraged margin trading, it comes down to your trading style and how much you can risk losing. A cross margin gives you more breathing room to recover with a larger risk-to-reward ratio. But in case of forced liquidations, you’ll lose the entire balance of your account.
An isolated margin, on the other hand, will bring the liquidation price much closer to your entry. But if a margin call happens, you only lose the margin for that particular position. If the price returns to your predicted direction, you’ll no longer be in the trade to reap the benefits.
Liquidation Price
We’ve been referring to liquidation for quite a while now. In simple words, liquidation means that the price of one or more crypto assets has reached a price level where the lender’s funds are at risk. Hence, a margin call is issued.
It’s simple because no lender will not sustain any losses on behalf of the trader. An account maintenance margin includes a trading fee, liquidation fee, and interest before a margin call occurs. The result is a zero account balance. An insurance fund is also in place to cover the lender’s liabilities during margin calls.
Liquidation is the biggest risk for any leveraged trading position without proper risk management, especially in a cross-margin position. When liquidation occurs, it’s known as a margin call.
Interest/ Trading Fee
As you’re borrowing funds from a trading platform, you must pay interest on the margin loan. The severity of the interest will vary between crypto margin trading exchanges. Position opening and closing fees also occur in Bitcoin margin trading.
Order Types
In most margin trading exchanges, you can place three different types of orders.
- Market Order: Once chosen, the order is executed at the next best market price. Fees for market orders are generally higher than limit or stop-limit orders.
- Limit Order: A limit order is when a trader places a “limit” on the price for the order to execute.
- Stop-Limit Order: This conditional order is commonly used for stop loss to avoid a margin call. This allows more control to the trader on when the order should be filled, but it often suffers from slippage.
Long Positions vs. Short Positions
As mentioned, margin trading crypto allows a trader to profit from both price increases and decreases. It’s determined with long and short positions in crypto markets.
Long Position
A long position is when you speculate the cryptocurrency price will increase. You “buy” the contract at a low price and “sell” it when the price reaches your projected target. For example, if you open a long Bitcoin margin trading position with a 5x leverage and the price of BTC increases by 10%, you make a 50% profit on the position size.
Short Position
A short position is the opposite of a long one, where you’re speculating the underlying asset’s price will decline. You “sell” the contract at a higher price and “buy” it back when it reaches your projected bottom.
The opportunity to profit from price decline is one of the major attractions of derivatives trading, including Bitcoin margin trading.
Long Squeeze vs. Short Squeeze
When you put pressure on a piece of lime, the juice “squeezes” out to alleviate the pressure. A similar concept applies to squeeze in the crypto. When there are too many leveraged position traders either on the long or short side, whales may manipulate the price to trigger stop losses, reducing the leverage ratio.
When many traders get liquidated or hit the stop loss, a squeeze is very hard to predict. If you look at the price chart during a squeeze, you’ll notice sharp price movement against the direction of most traders. It’s a risk that doesn’t exist in the spot market.
Technical Analysis for Margin Trading Cryptocurrency
Unlike crypto spot trading, margin trading is not intended for the long term. It also makes sense because it’s a higher-risk approach to trading cryptocurrencies than spot trading. This is why technical analysis (TA) precedes fundamental analysis (FA) regarding trading methods.
Also, many veteran traders believe that fundamental news is often baked into the price action if you know how to interpret it.

Tools for Technical Analysis
Success in trading cryptocurrency comes from stacking the odds in your favor. TA aims to give as many confluences as possible to support your crypto trading decision. As for the tools you should use, it’s an empty canvas.
Some traders have seen success in using moving average crosses. Another group of traders may believe in overbought/oversold conditions of the market as a trigger. Many traders strictly stick to price action as it’s the leading indicator in crypto exchanges.
The most amazing thing is all of these groups are right in their position. As long as they’re making profits from margin trading using their approach, we cannot invalidate them.
We’re trying to establish here that you must decide which tools you want to use first. Your next task is to learn them by heart.
Then, you devise a crypto trading strategy using the tools you’ve learned. The most important part of the strategy is backtesting. The risk-to-reward ratio of the strategy will determine the win rate you need to be profitable.
For example, a strategy that gives you 1:3 RR will be profitable even if you lose more than half of your trades. But it must be proven based on historical data that your system works.
The last step is to forward-test your strategy in real time to see if the conditions work.
Risk management is a crucial aspect of crypto trading, so we’ve created a dedicated section in our guide to crypto margin trading.
The Importance of Risk Management
According to current statistics, almost 95% of day traders lose money consistently. Only 5% have figured out how to get an edge over the market with trading strategies.
The secret has always been risk management. Without proper risk management, what you do will be considered “random reinforcement.” You start to believe that you know what you’re doing. Suddenly, you’ll lose all your profits in a bad trade.
A proper risk management plan will give your trading behavior the needed structure. You enter with a fixed margin; you exit after a certain percentage of profit or loss. What the market does in real-time becomes a secondary concern, removing the emotionally exhausting aspect of margin trading.
A risk management plan usually has three different components.
- Position Size
- Leverage Ratios
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio

Position Size
This is the currency amount you’re risking per trade. You can keep it uniform or use a percentage of your total portfolio. Successful margin traders use 1% to 2% of their account as the position size.
Leverage Ratios
The leverage you use for one position plays a dramatically important role. Margin calls are often the result of overleveraged positions. You must understand that leverage increases your profit potential and involves a significant liquidation risk.
For example, let’s assume you opened a long position on BTC with 10x leverage at $25,000. For the amount you have in your account, the liquidation price is $13,000. But if you bump up the leverage to 100x, the liquidation price will come to a lot closer, $20,000, perhaps.
BTC can go to a lower price of $20,000 overnight. But it’s unlikely that it’ll go to $13,000. Hence, leverage plays a crucial role in limiting risk.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio
This is the ratio of the money you’re risking and the money you’re making from a particular margin trade crypto. A 1 to 3 risk-to-reward means you’re risking 1 unit to win three units. The great thing about bigger RR is that your strategy doesn’t need an unrealistic win rate.
Success in the margin or crypto spot trading comes down to the numbers game. If the numbers support your profitability, you’ll be profitable. The challenge is eliminating emotions from trading and sticking to the system you develop with your funds.
Margin Trading vs. Spot Trading
One of the fundamental differences between margin trading and spot trading is that margin trading allows you to profit in both directions. You can open long positions when you believe the price will increase and short selling positions when you suspect a market decline.
In spot trading, on the other hand, you can profit only when the market moves in one direction, the upside. On the bright side, you own the asset you buy with your money rather than a margin contract, so you can’t get liquidated in a spot market.
Summary
If a trader can continuously develop the discipline to stick to a system, margin trading allows exponential gains compared to spot markets. The profits are not nearly as lucrative when you trade with your funds.
Sure, you’re paying the interest rate and involving more risk with a leveraged position than a spot trade. But as long as you respect a certain threshold with risk management, a margin trade is no riskier than spot trade in crypto markets.
Crypto margin trading involves substantial risk, and numerous investors have incurred losses far greater than they could bear due to their misunderstanding of the profound risk of augmented losses in a volatile market.
What exactly is Crypto Margin Trading? It's a method that involves the use of borrowed capital for trading. The primary distinction from spot trading is that margin trading enables traders to initiate a position without contributing the entire sum from their own funds.
Leverage ratio of 10:1, also depicted as 10x, empowers a trader to execute a trade worth tenfold the amount of their collateral. Hence, a down payment of $50 would facilitate a trade amounting to $500.