What Is a Liquidity Pool?
Liquidity pools are tokens locked in smart contracts that provide liquidity in decentralized exchanges to attenuate the problems caused by the illiquidity typical of such systems.
Liquidity pools are also the name given to the intersection of orders which create price levels that — once reached — see the asset decide whether to continue to move in an uptrend or downtrend.
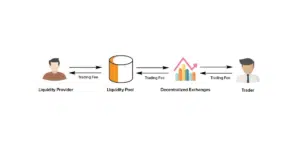
Liquidity Pool Explained | Source: Coinsutra
Decentralized Exchanges
The decentralized exchanges that leverage liquidity pools are the same that make use of automated market maker-based systems.
On such trading platforms, the traditional order book is replaced by pre-funded on-chain liquidity pools for both the assets of the trading pair.
Efficient Trading Across Assets
The advantage of using liquidity pools is that it does not require a buyer and a seller to decide to exchange two assets for a given price, and instead leverages a pre-funded liquidity pool.
This allows for trades to happen with limited slippage even for the most illiquid trading pairs, as long as there is a big enough liquidity pool.
The funds held in the liquidity pools are provided by other users who also earn passive income on their deposit through trading fees based on the percentage of the liquidity pool that they provide.
One of the first decentralized exchanges to introduce such a system was the Ethereum-based trading system Bancor, but it was widely adopted in the space after Uniswap popularized them.