Understanding Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
An automated market maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol that enables users to buy and sell digital assets directly without a third-party intermediary.
The primary function of AMMs is to automate the process of pricing and matching orders on the exchange, utilizing algorithms to determine asset prices and facilitate trades between buyers and sellers.
This decentralized approach allows for trustless, peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating the need for custodians or other intermediaries.
AMMs are popular due to their simplicity, user-friendly interfaces, and low transaction fees.
Traders can swiftly open and close positions without grappling with complex order types or matching mechanisms typically found in traditional exchanges.
Moreover, AMMs often offer enhanced speed and security as they leverage smart contracts and operate on blockchain networks.
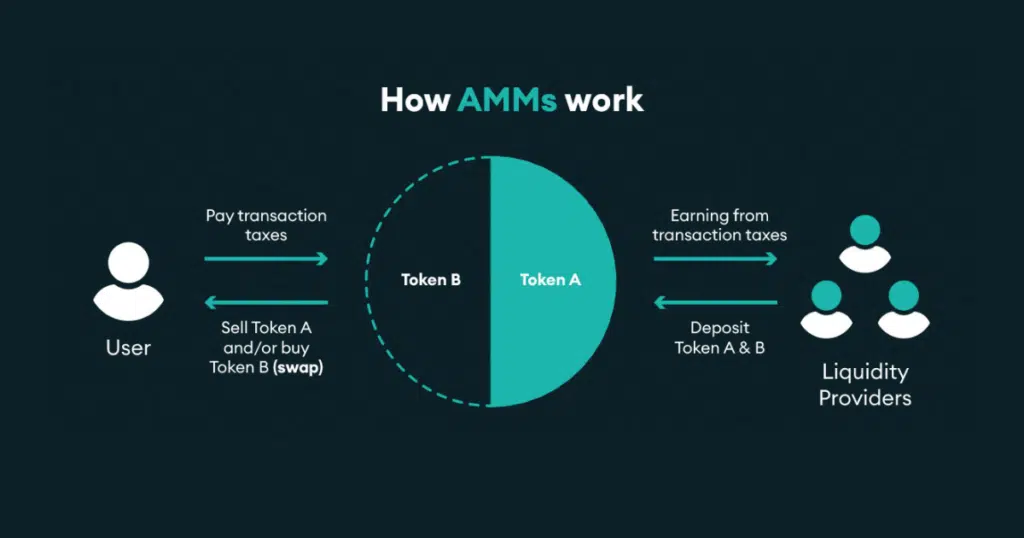
AMM and Order Book Model
The key distinction between an AMM and an order book model lies in the mechanism for price determination.
In an AMM, liquidity pools automatically set prices based on the available liquidity.
On the other hand, an order book model relies on buyers and sellers setting their prices, facilitating price discovery.
By leveraging the liquidity pool’s automated mechanism, AMMs eliminate the need for manual price setting.
In contrast, an order book model requires market participants to manually set prices and create orders for buying and selling assets.
Additionally, AMMs generally offer lower fees and improved liquidity than order book models.
Pros and Cons of AMMs in DeFi
Pros:
- The AMM model offers a more efficient alternative to traditional order book exchanges, enabling direct trading of digital assets without intermediaries.
- AMM’s liquidity pools allow trade without counterparties, enhancing accessibility.
- AMMs are highly automated, eliminating the complexities associated with manual order book management.
- Traders benefit from low fees as the system operates with minimal costs.
- AMMs offer increased liquidity compared to traditional exchanges, improving trading opportunities.
Cons:
- AMMs are susceptible to price slippage and impermanent loss, potentially resulting in significant losses for traders.
- AMMs often have limited asset offerings, restricting access to markets available on traditional exchanges.
- Malicious actors can exploit the automated nature of AMMs.
- AMMs can be complex to understand and use, posing challenges for some users.
- As a relatively new concept, AMMs carry the risk of bugs or vulnerabilities in their code.
- Regulation of AMMs is not always in place, potentially leaving users unprotected in case of hacks or scams.